In S/4HANA 2022, SAP introduced a tool called “Organizational Flexibility in Financial Accounting” (also called “Organizational Change” or “Profit Center Reorganization”) which enables the changing of legal and management entities that are grouped according to organizational structures, master data and transactional data. This feature allows you to update the profit center assignment in master data, such as Materials, Assets, WBS Elements CO Orders, and creates transfer postings for selected balance sheet accounts and open payables and receivables. Watch this recorded webcast with SAP FI/CO Expert Paul Ovigele to learn the following:
- The various scenarios where Profit Center Reorganization is needed.
- How to use the “Manage Organizational Changes” app is to help you to split, combine, and replace profit centers.
- Which SAP Objects are affected by the reorganization.
- How you can navigate to related apps for organizational changes.
- Limitations of the “Organizational Flexibility in Accounting” feature.
SAP ECC Classic GL to SAP S/4HANA – Direct Conversion Without Requiring a New GL Migration First
The new General Ledger on SAP S/4HANA or ECC has certain advantages over Class GL. Examples: usage of parallel ledgers, Document splitting, Profit Center Financial statements, Segment' reporting that is required for segment reporting according to IAS and U.S. GAAP, etc. In addition, Customers can enhance the new General Ledger flexibly, that is, they can enter user-defined fields and update the relevant totals. Many standard reports can evaluate the information from the user-defined fields. Customers can use the 'Document Splitting' functionality to create financial statements at the company code level and, if required, for entities, such as the segment. As a result, we no longer have to carry out time-consuming reconciliation tasks between FI and CO for the end of the period since cross-entity processes are transferred in real-time to the new General Ledger in Controlling.
Starting from 1709, In new installations of SAP S/4HANA, the new General Ledger Accounting is activated by default. The existing ECC customers moving from SAP ECC to SAP S/4HANA will also get new GL automatically. As a result, ECC customers will also move to New GL on SAP S/4HANA Conversion. However, they cannot implement document splitting or a further accounting principle/ledger during the conversion project. The architecture of the accounting module in SAP S/4HANA from the 1709 version is based on the concept of the former "New GL". The concept of the Subsequent Implementation of Document Splitting in SAP S/4HANA differs from the Migration Scenario 6 of the "New GL".
“Professionalized Business Case” is the first step of SAP S/4HANA Journey!
SAP provides mainstream maintenance for core applications of SAP Business Suite 7 software including SAP ERP 6.0, SAP Customer Relationship Management 7.0, SAP Supply Chain Management 7.0, and SAP Supplier Relationship Management 7.0 applications and SAP Business Suite powered by SAP HANA on the respective latest three Enhancement Packages (EhPs) until December 31, 2027. From January 1, 2028, all SAP Business Suite 7 core applications and respective SAP Business Suite 7 add-on products will enter the customer-specific maintenance (CSM) phase. SAP offers an optional extended maintenance phase from January 1, 2028, until December 31, 2030. This three-year phase comes at an additional fee on top of the maintenance fee. Details outlined in SAP Note 2881788.
Asset Accounting in SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA has brought about a number of improvements in Asset Accounting. There is a tighter integration with Finance, and postings are now real-time, updating all ledgers at the same time as the asset, allowing a smoother period end and an easier migration.
This is a new webcast, to update the original “Ask a Fixer: What You Should Know About New Asset Accounting with SAP S/4HANA” created in 2017. It explains the previous material in a new way, and in addition, covers new transactions for closing and migration. It also introduces the new Fiori “experience”, which brings additional functionality such as the asset accounting overview and embedded analytics.
Executing the Steps for Migrating to S/4HANA Finance
One of the key tasks when migrating to S/4HANA is to convert your Financial data from the old tables in ECC to the new tables (particularly the Universal journal) in S/4HANA. This process usually takes place after the technical upgrade from ECC to S/4 and is done during a downtime period. It involves a series of transactional steps that are executed in sequence, with progression to the next step only possible when a previous step has been executed successfully or confirmed. Several iterations of a Finance Migration need to be done in a Sandbox (or test) system in order to resolve any issues that arise. This will therefore make the eventual Production migration smoother and easier to accomplish during the downtime window. It is therefore important to know what steps are carried out and the types of errors that could occur.
Q&A: Enable Cost Component Split in G/L Accounts – Before SAP S/4HANA!
The Cost Component Split allows for granularity of the cost drivers in your inventory and cost of goods sold. The cost components can be seen in various reports in Product Cost Planning and Material Ledger. However, this breakdown has not been available in the General Ledger before SAP S/4HANA. By utilizing a Custom Enhancement, the Cost Component Split by G/L Account can be available in the ECC system. This will provide suitable transparency about cost drivers in the General Ledger, particularly for companies that do not plan an S/4 conversion for a few years, and also positions them with a Splitting Structure that is compatible for an eventual S/4 Conversion. This functionality can be used to split cost components for COGS accounts as well as Inventory accounts (which means that you can get transparency into how much material stock or Fixed costs are sitting in inventory). Also, this functionality can be used whether a company uses Material Ledger or not (i.e. it can be used for Standard and/or Actual cost components). Watch this pre-recorded live Q&A with FI/CO expert Rogerio Faleiros to learn:
The things to consider when deciding whether to split COGS in the G/L Accounts.
How to map the original COGS account to the Cost Component Split Accounts.
A demo of the Cost Component G/L Split program and how to view the General Ledger postings.
The Reports that can be used to display the COGS documents that have been split.
Q&A: Costing vs. Account Based CO-PA – Understanding the Differences In ECC & S/4 HANA (Part 1)
THIS PRESENTATION WITH Marjorie Wright WILL COVER:
What is the difference between Costing and Account Based CO-PA?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Costing vs. Account Based CO-PA?
What are the implications of activating both types of CO-PA?
What are the steps to transition from one type of CO-PA to the other?
Which type of CO-PA is compatible with the Universal Journal in S/4 HANA?
How much CO-PA detail is now posted to the Universal Journal?
Speaker:
Marjorie Wright, FI/CO Expert, SimplyFI-CO, LLC
What's Changing in FSCM - Dispute Management in S/4HANA Compared to ECC
I wish for a world without any dispute, but the reality is that in every sphere of business there are chances of dispute. While running a business, customer disputes can impact organization’s financial stability and creditability.
SAP FSCM - Dispute Management helps in identifying and documenting disputes earlier in the payment cycle, track and monitor reasons that drive DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) and streamline process of dispute resolution while fully integrated with FI. Key process steps in FSCM - Dispute Management are as below:
FSCM - Dispute Management is not a new functionality and was existing in ECC environment also, so what’s really changing in FSCM is of great interest for organizations converting/adopting S/4HANA. Let’s see key changes in detail:
Transactional Simplifications
The core attributes of dispute case are the same in S/4HANA as in ECC, but the transaction processing has been simplified a lot in S/4HANA. See below highlights of such transactional changes:
Process Receivables (Fiori ID F0106)
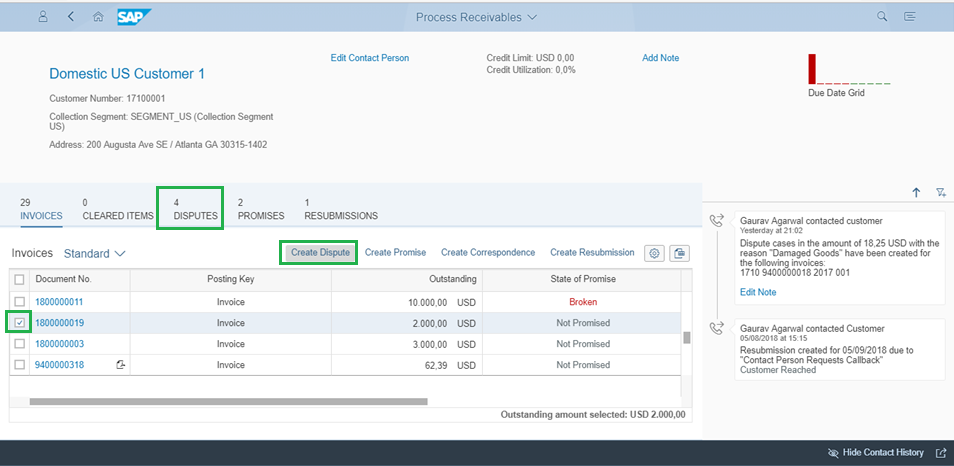
Process receivables Fiori application is under FSCM - Collection Management, but fully integrated to FSCM - Dispute Management. E.g. in below Figure 1 for Process Receivables app, you have the option to see the dispute cases for the customer and can also create new dispute cases for outstanding items.
Figure 1: Dispute Management integrated to Collection Management
When creating the dispute case, the screen as showing in Figure 2 below is also having very specific relevant fields for user to create the dispute case:
Figure 2: Simplified entry screen for dispute case creation
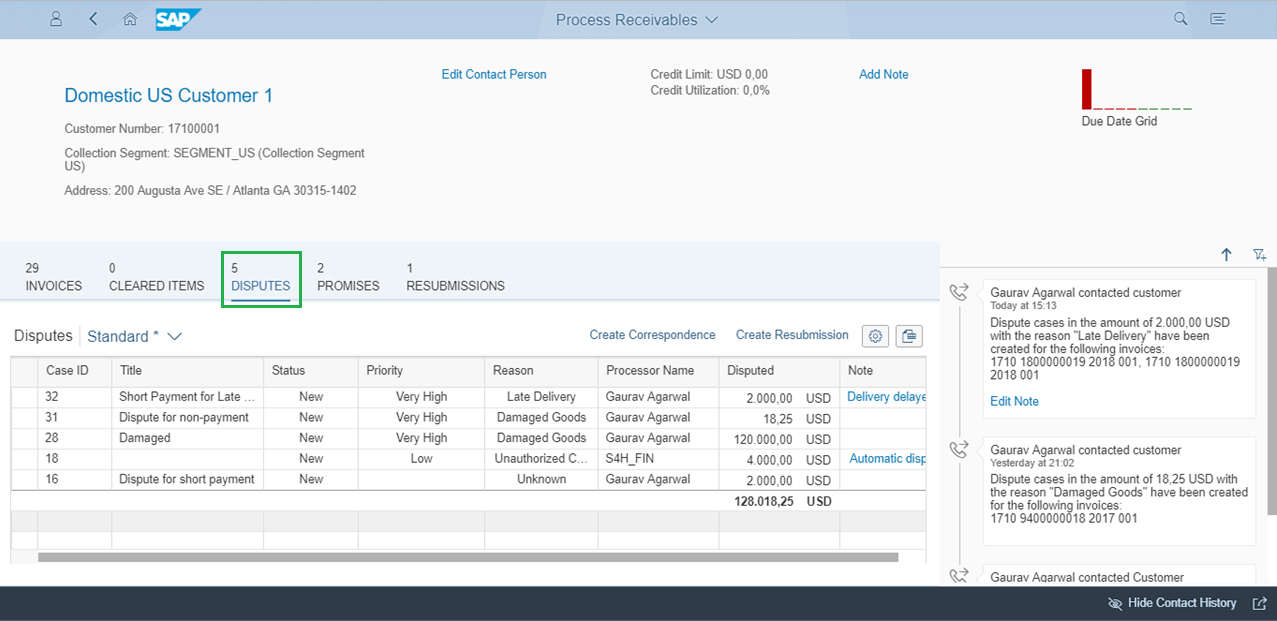
Various disputes for the custom will appear at the same place as shown in Figure 3 below:
Figure 3: Displaying dispute cases for the customer in Process Receivables app
Manage Dispute Cases (Fiori ID F0702)
This fiori application helps in managing the dispute cases as shown in Figure 4 below. Here you can change the processor for multiple dispute cases in single go. Or can go inside the particular dispute case to change its’ attributes:
Figure 4: Unified dashboard to show various dispute cases to process
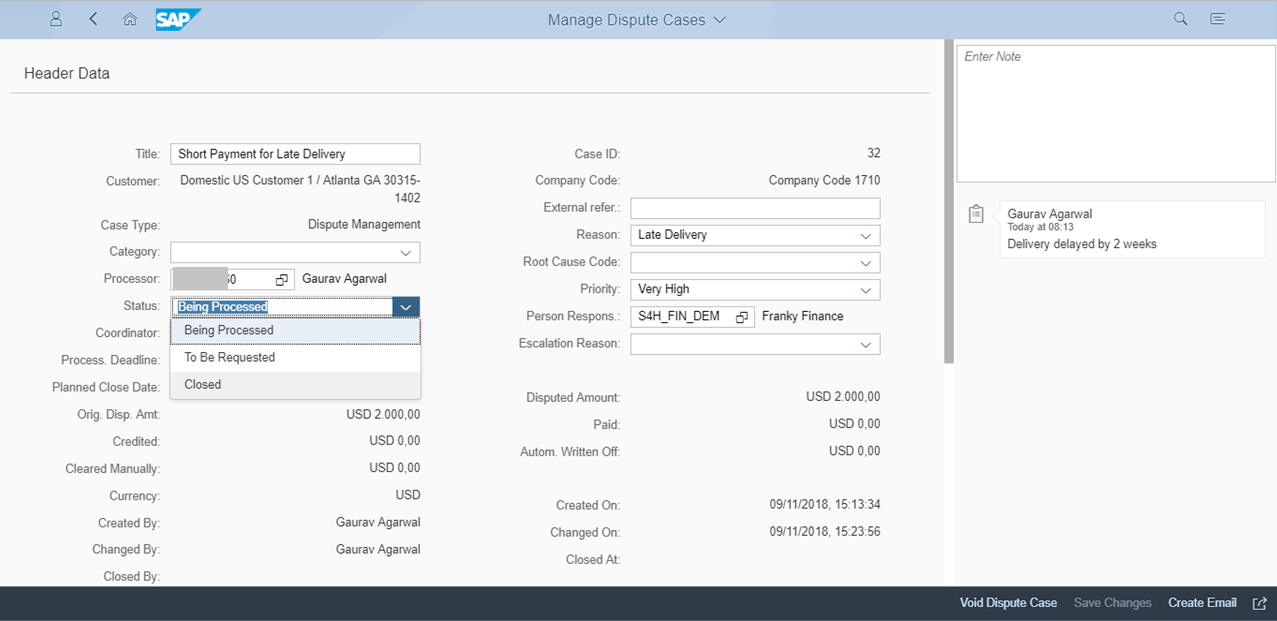
On opening a dispute case, you can change the other attributes like root cause code, person responsible, reason etc. as shown in Figure 5 below (The attributes are same as in ECC environment.)
Figure 5: Changing the attributes of a dispute case
Other Fiori Applications of GUI type:
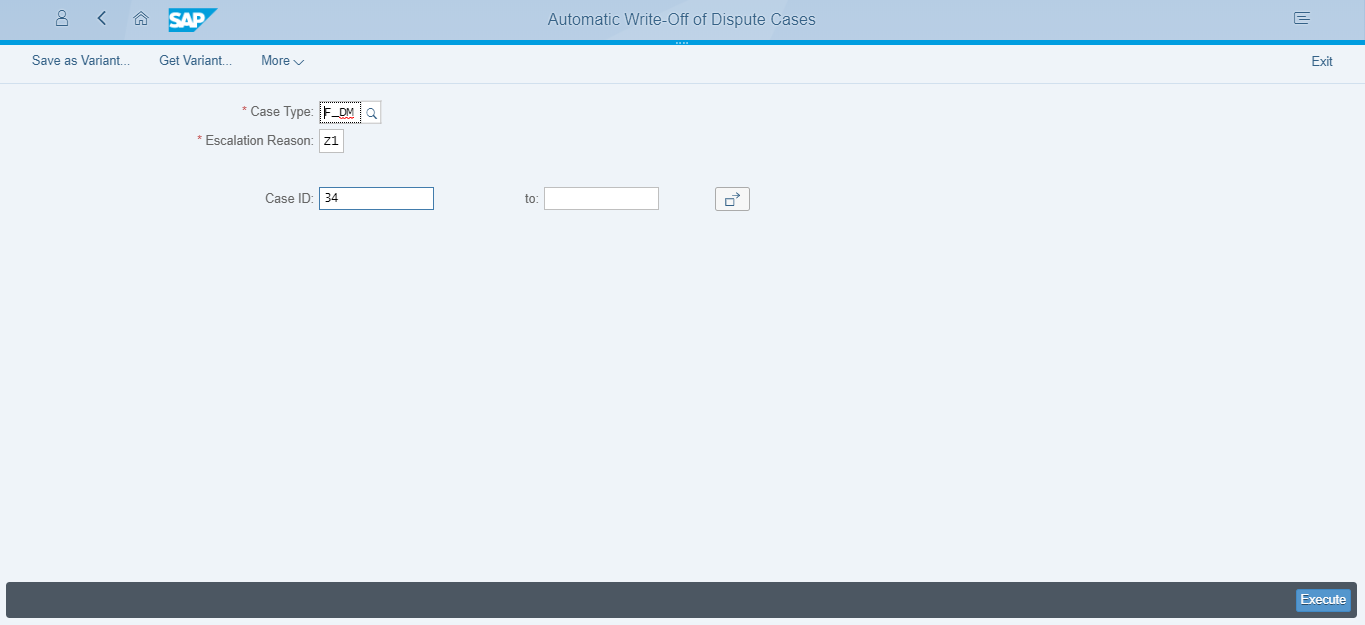
There are various other fiori applications available, like Write off dispute cases (Fiori ID UDM_AUTOWRITEOFF) which are of GUI type, i.e. the look and feel is similar to SAP GUI transaction codes so the processing will not be impacted in S/4HANA environment for such transactions. For example, Figure 6 show the screen like GUI transaction UDM_AUTOWRITEOFF
Figure 6: Fiori application of GUI type
Analytical Innovations
Analytical power is core capability in S/4HANA and it provides a lot of out-of-the-box analytical applications, which shows the key KPIs on the tiles page as shown in Figure 7 below:
Figure 7: Analytical apps showing KPI information for dispute management
Let’s see some more drilldown into these analytical apps on what kind on information these are showing:
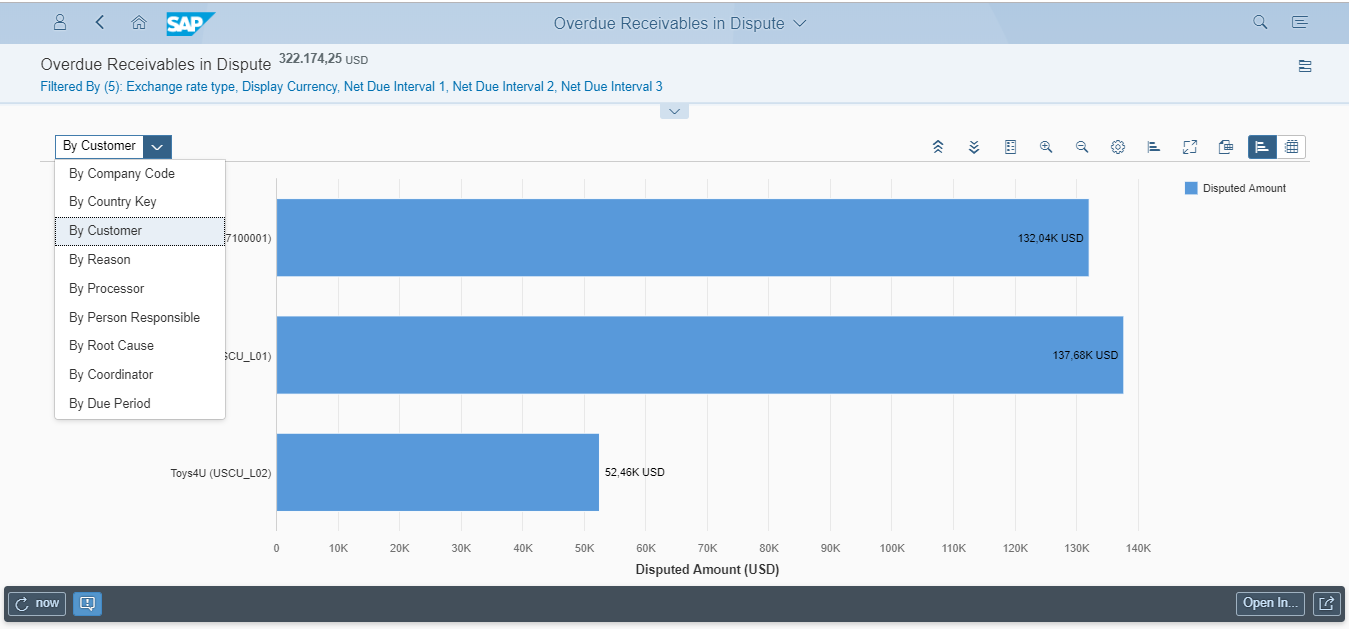
Overdue Receivables in Dispute (Fiori ID F2540)
Figure 8 show the overdue receivables in dispute cases and thus represent directly the working capital having less probability of realization. The analysis can be done from various angles, like by company code, by customer, by processor etc.:
Figure 8: Fiori application - Overdue Receivables in Dispute
Open Disputes (Fiori ID F1752)
Figure 9 show the open dispute cases and analysis can be done from various angles, like by customer, by processor etc.:
Figure 9: Fiori application - Open Disputes
Solved Disputes (Fiori ID F2521)
Figure 10 show the closed dispute cases and analysis can be done from various angles, like by processor, by dispute case, by processor etc.:
Figure 10: Fiori application - Solved Disputes
Processing Days of Open Disputes (Fiori ID F2522)
Figure 11 show the processing days of open disputes and thus helps in prioritization of the cases for follow-up. The analysis can be done from various angles, like by coordinator, by dispute case, by customer etc.:
Figure 11: Fiori application - Processing Days of Open Disputes
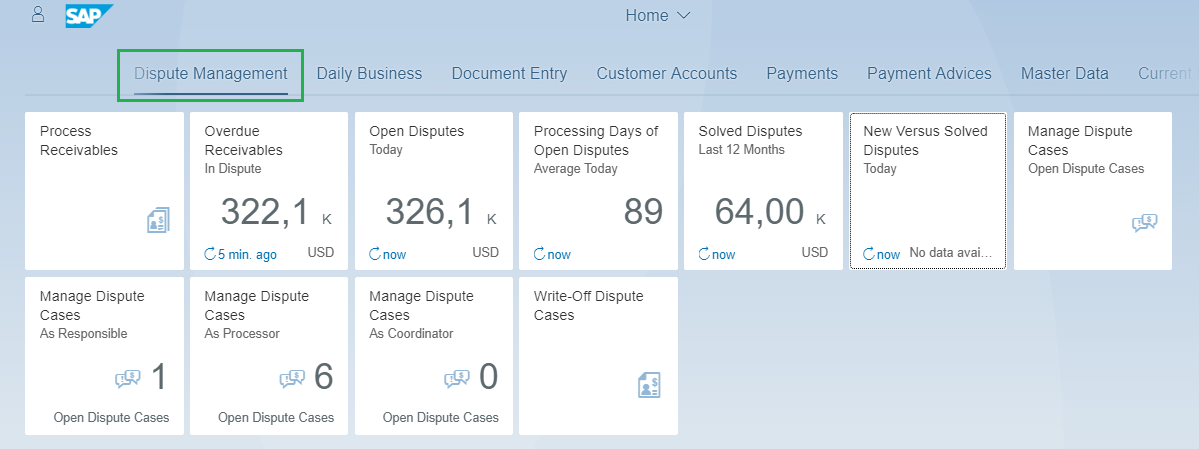
Role based menu in Fiori Launchpad
SAP S/4HANA provides Fiori Launchpad and thus all the related fiori applications for the user to manage dispute cases can be placed in single catalogue for ease of processing as illustrated in below Figure 12:
Figure 12: Fiori application - Processing Days of Open Disputes
Integration with external application(s)
You can define external applications that allow you to process dispute cases outside of SAP Dispute Management. In the out-of-the-box settings, the SAP application “CRM Claims Management” is defined as an external application.
Lighting fast processing powered by HANA platform
FSCM – Dispute Management is also not secluded from proven processing speed benefit of HANA.
The processing in new transactional apps is faster because of simplified accounting data structure in backend, fewer data fields to fill and fewer steps to perform the dispute transactions.
In a nutshell, S/4HANA increases the utility for dispute management function and intensify the business case compared to using any third-party tool for this function.