The Embedded Analytical tools may be divided based on usage. CDS Views are the foundation for all analytical applications. Programmers create a virtual data model using CDS views. In comparison, the key user uses CDS views to create dashboards. "Custom Analytical Queries" will be used to develop customer queries. Finance and Logistics end users. Use reports and dashboards created by the key user. Functional users will use SAP Smart Business Cockpits with predefined content for different multidimensional reports across all business lines.
Some multidimensional reports provide to end-users through SAP Fiori. They have flexible slice-and-dice navigation features. "Query Browser" will help end-users for analytic queries that allow them with flexible slice and dice reporting. "View Browser" is another tool to check the delivered CDS Views and Queries. These tools help the Functional team ( Finance, Logistics, ………… users) to get reports with no latency, no data duplication, excellent performance for all types of reports, Integration scenarios with SAP BW, and also Support for SAP ERP authorizations.
1. Report Design Modeler — Apps
*See picture 1 labeled below
The Report Design Modeler apps are a set of SAP Fiori apps that customers can use to create and manage Financial or Logistics or any other reports. When created an evaluation, we choose a tile to visualize the reports in the Publish Report app.
*See picture 2 labeled below
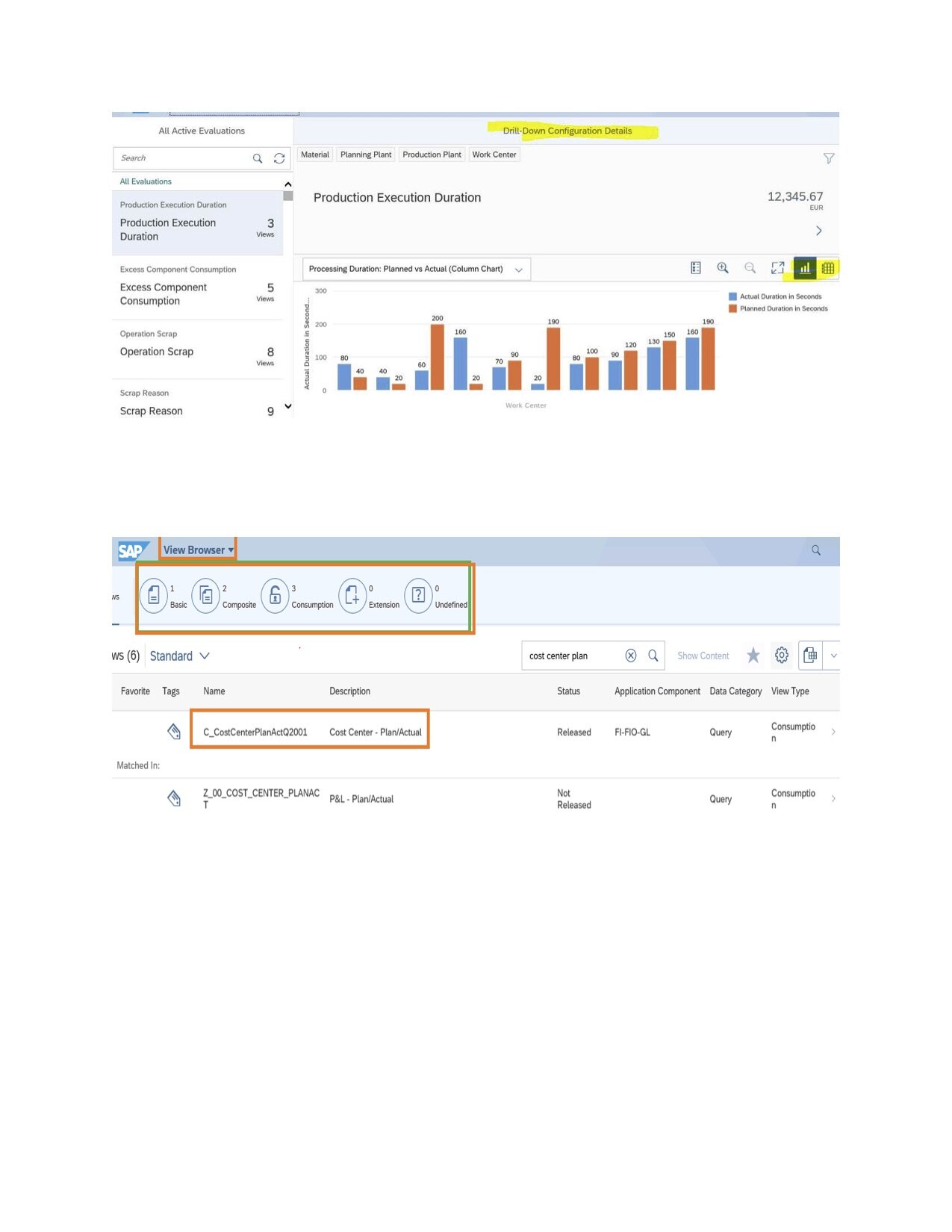
You define this using the Configure Report Drill-Down app.
*See picture 3 labeled below
Business knowledge helps to configure the drill-down views. Configure Report Drill-Down app is used by power users who can see data in Graphs IT administrative knowledge is needed to authorize users to get access to these reports
You may use this capability for all most all Finance reports like:
Analyze Actual Cash Flow, Liquidity Forecast, Budget Alerts, Contract Expiry, Aging Analysis,
Analyze Change Impact, Analyze Collections Success, Analyze Collections Volume, Analyze Credit Exposure, Analyze Open Credits, Analyze Overdue Items / Overdue Item Analysis, Analyze Payment Locks, Analyze Payment Run Exceptions, Cash Discount Utilization, Cash Discount Forecast, Cash Collection Tracker - Accounts Receivable, Cash Position, Analyze Returns, Operational Supplier Evaluation / Supplier Evaluation, Payment Statistics, Credit Limit Utilization, Days Payable Outstanding Analysis,
Days Sales Outstanding, Detect MRP Situations, Future Receivables, Future Payables……….Etc.
2. Overview of View Browser and Query Browser
The View Browser
View browser allows Power users from all business lines to explore thousands of VDM views without any technical skills. So, it helps Business Users to draw meaningful reports for their business requirements. You can find suitable views based on your need and display its content for analytical queries in Design Studio. Using View Browser, we can explore standard Core Data Service views (Composite and Consumption) and create developers.
+
*See picture 4 labeled below
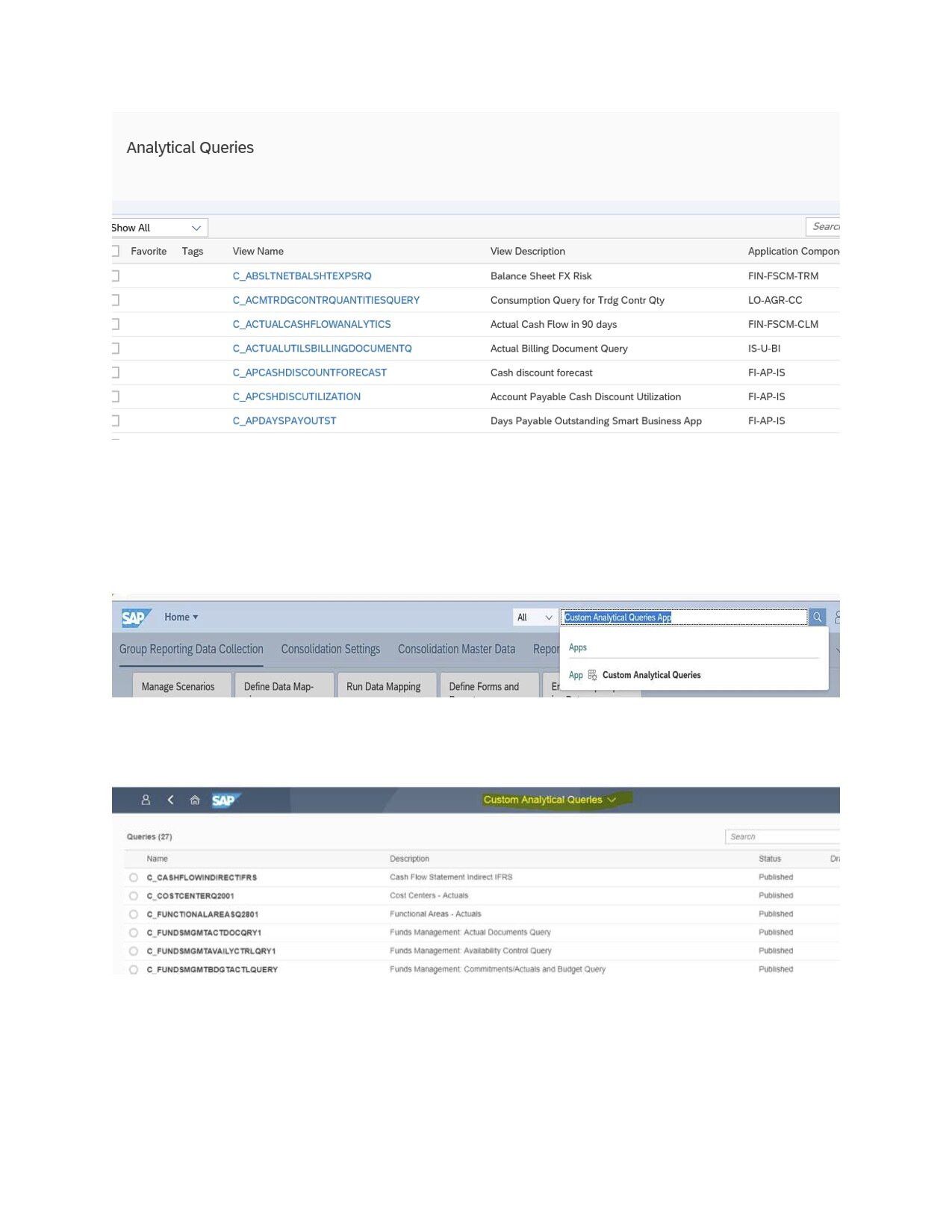
The Query Browser
The Query Browser is a default Design Studio app that is available in the standard SAP Fiori Library.
The Query Browser is not part of the SAP Fiori launchpad's default view and is added to the My Home group. The Query Browser will show consumption views that were annotated as Analytical Query and therefore act as a source for KPIs. Users can select an Analytical Query and perform on-demand reporting on it.
The Query Browser is a default Design Studio app available in the standard SAP Fiori Library. No additional installation is required.
In the Query Browser, you can see many analytical queries.
*See picture 5 labeled below
Business catalog SAP_CA_BC_VDM is to assigned to the user.
3. Custom Analytical Queries app
For creating Financial or Logistics or a report that is needed from any business line, from scratch, SAP provides the built-in, easy-to-use, Custom Analytical Queries app. It is aimed at key users, rather than end-users. An advantage of it is that you don't have to understand the query language to build a query.
*See picture 6 labeled below
Required Business Role: SAP_BR_ANALYTICS_SPECIALIST
Required Technical Catalog: SAP_BASIS_TCR_T
Activated ICF node: ANA_QDESIGN_MAN (ICF path /sap/bc/ui5_ui5/sap/ana_qdesign_man)
Example: Power-user wants a report from Cost Center Module.
Customers can create a Custom Analytical Query to report in Cost Center Module on Actual Vs. Plan data. We can also have a drill-down facility
*See picture 7 labeled below
4. The Report Designer Modeling apps
The Report Designer Modeling apps are a set of SAP Fiori apps that a key user uses to define or manage reports.
*See picture 8 labeled below
These Reports are based on the Analytical List Page Smart Template.
Customers can Create Reports using create report app based on measures of the related Analytical Query.
Just enter the relevant data source details such as the Core Data Services (CDS) view, the OData service path, and the entity set that corresponds to the CDS view.
*See picture 9 labeled below
Choose Activate and Add Evaluation.
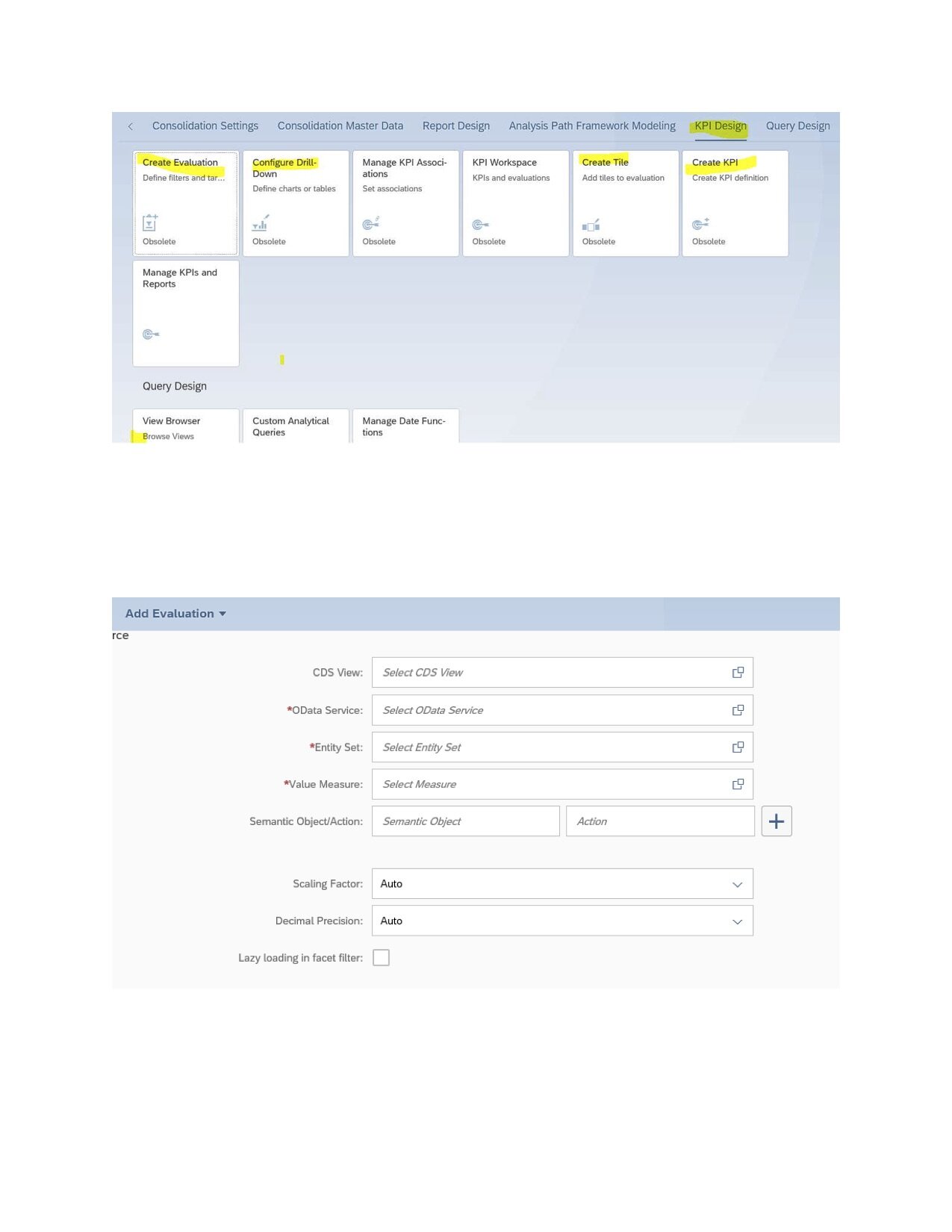
5. The KPI designer - Smart Business Framework
SAP Fiori Smart Business helps customers create their analytical apps based on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
*See picture 10 labeled below
Smart Business Cockpits can be personalized. They bring analytics into the business process when the user needs it. Customers can develop an Analytical Query to analyze business data using the KPI Designer tool.
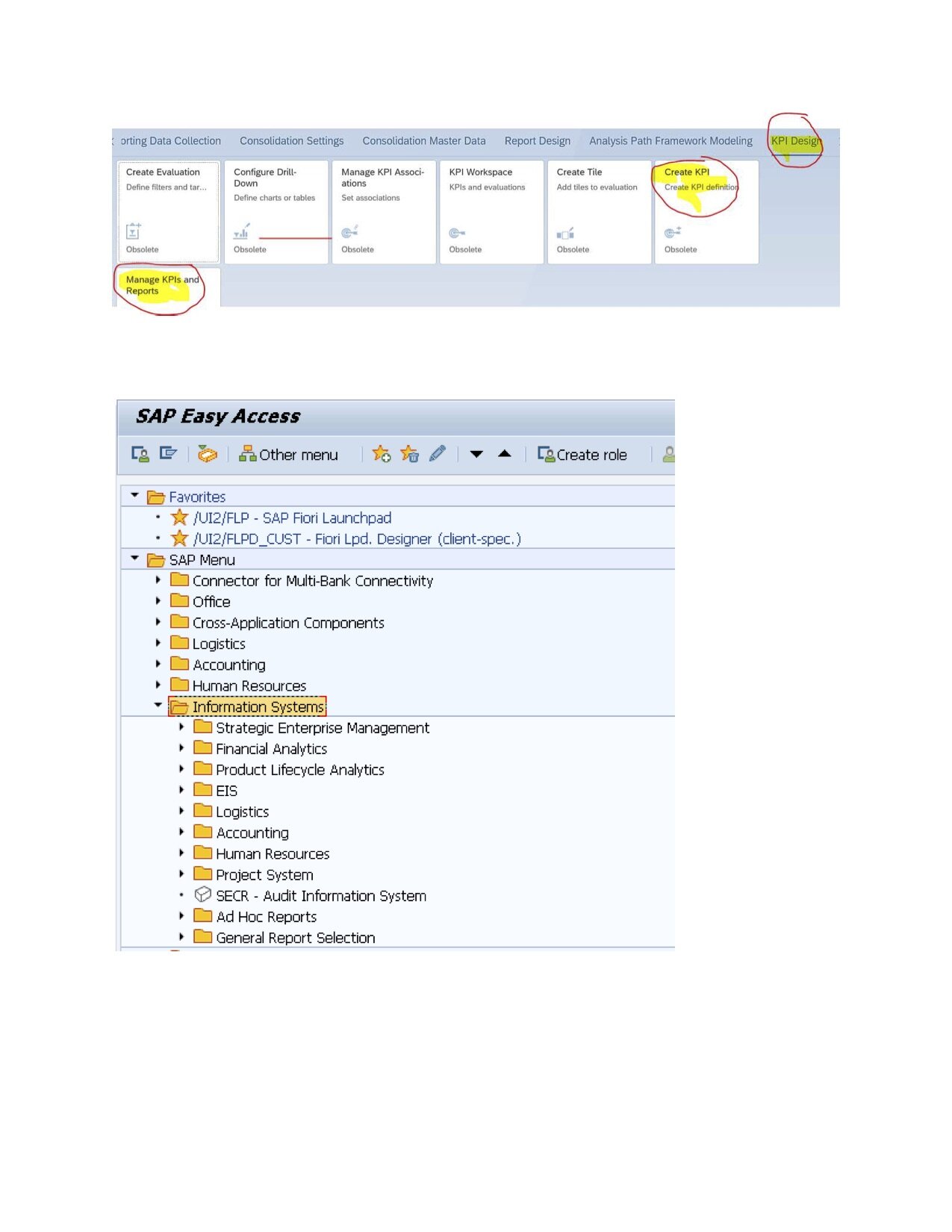
You can create a KPI, in the following order:
· Create KPI
· Create Evaluation
· Create Tile
· Configure Drill-Down
· Manage KPI Associations (optional)
6. SAP Analytics UIs
SAP Analysis for Microsoft Office is a Microsoft Office Add-In that allows multidimensional Analysis When you install Analysis for Microsoft Office on your local machine; you can connect directly to the following:
SAP Business Warehouse (BW) system
SAP Business Objects Business Intelligence (BI) Platform
SAP HANA
Using Analysis for Office, you can also access Core Data Services view based queries and view the report.
7. SAP delivers several standard reports.
You can find these reports at various locations under the Information System in the SAP Easy Access menu.
*See picture 11 labeled below
Almost every application in the system has an Information System menu option, which contains the reports predefined by SAP. You can also display thru SE43.
*See picture 12 labeled below
You can search standard reports in SE38, by the letters they contain. For example,
Vendor related reports can are found by RFK*
Customer-related Reports can be searched by letter RFD*
General ledger RFS*
Document Reports: RFB*